AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Professional v1.0
Question 1
You have deployed a web application targeting a global audience across multiple AWS Regions under the domain name.example.com. You decide to use
Route53 Latency-Based Routing to serve web requests to users from the region closest to the user. To provide business continuity in the event of server downtime you configure weighted record sets associated with two web servers in separate Availability Zones per region. Dunning a DR test you notice that when you disable all web servers in one of the regions Route53 does not automatically direct all users to the other region.
What could be happening? (Choose two.)
- A. Latency resource record sets cannot be used in combination with weighted resource record sets.
- B. You did not setup an HTTP health check to one or more of the weighted resource record sets associated with me disabled web servers.
- C. The value of the weight associated with the latency alias resource record set in the region with the disabled servers is higher than the weight for the other region.
- D. One of the two working web servers in the other region did not pass its HTTP health check.
- E. You did not set "Evaluate Target Health" to "Yes" on the latency alias resource record set associated with example com in the region where you disabled the servers.
Answer : BE
Explanation:
How Health Checks Work in Complex Amazon Route 53 Configurations
Checking the health of resources in complex configurations works much the same way as in simple configurations. However, in complex configurations, you use a combination of alias resource record sets (including weighted alias, latency alias, and failover alias) and nonalias resource record sets to build a decision tree that gives you greater control over how Amazon Route 53 responds to requests. For more information, see
How Health Checks Work in Simple Amazon Route 53
Configurations -
.
For example, you might use latency alias resource record sets to select a region close to a user and use weighted resource record sets for two or more resources within each region to protect against the failure of a single endpoint or an Availability Zone. The following diagram shows this configuration.
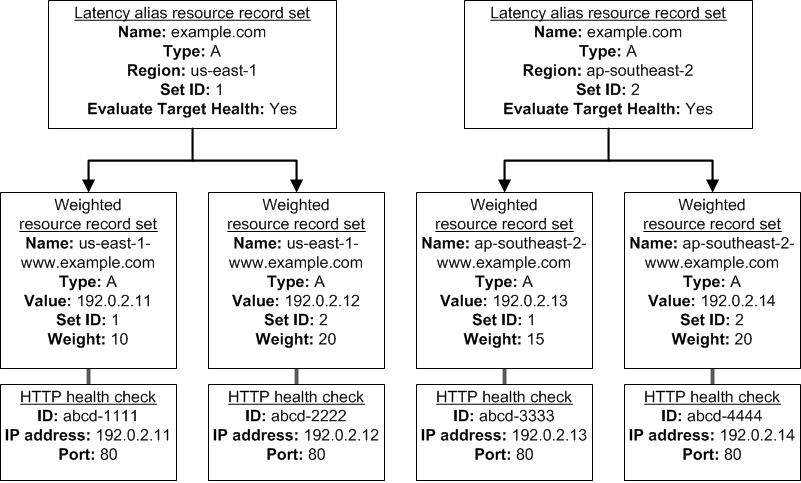
Here's how Amazon EC2 and Amazon Route 53 are configured:
You have Amazon EC2 instances in two regions, us-east-1 and ap-southeast-2. You want Amazon Route 53 to respond to queries by using the resource record sets in the region that provides the lowest latency for your customers, so you create a latency alias resource record set for each region. (You create the latency alias resource record sets after you create resource record sets for the individual Amazon EC2 instances.)
Within each region, you have two Amazon EC2 instances. You create a weighted resource record set for each instance. The name and the type are the same for both of the weighted resource record sets in each region.
When you have multiple resources in a region, you can create weighted or failover resource record sets for your resources. You can also create even more complex configurations by creating weighted alias or failover alias resource record sets that, in turn, refer to multiple resources.
Each weighted resource record set has an associated health check. The IP address for each health check matches the IP address for the corresponding resource record set. This isn't required, but it's the most common configuration.
For both latency alias resource record sets, you set the value of Evaluate Target Health to Yes.
You use the Evaluate Target Health setting for each latency alias resource record set to make Amazon Route 53 evaluate the health of the alias targetsג€"the weighted resource record setsג€"and respond accordingly.
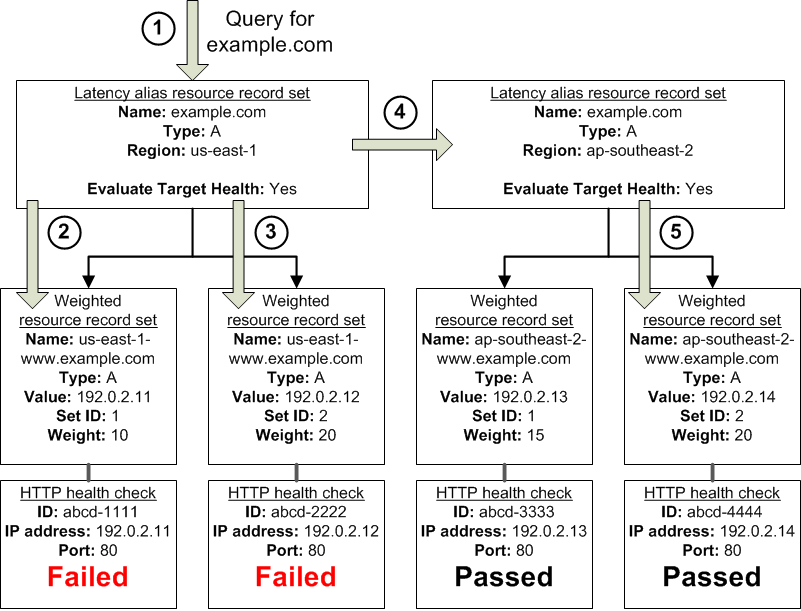
The preceding diagram illustrates the following sequence of events:
Amazon Route 53 receives a query for example.com. Based on the latency for the user making the request, Amazon Route 53 selects the latency alias resource record set for the us-east-1 region.
Amazon Route 53 selects a weighted resource record set based on weight. Evaluate Target Health is Yes for the latency alias resource record set, so Amazon
Route 53 checks the health of the selected weighted resource record set.
The health check failed, so Amazon Route 53 chooses another weighted resource record set based on weight and checks its health. That resource record set also is unhealthy.
Amazon Route 53 backs out of that branch of the tree, looks for the latency alias resource record set with the next-best latency, and chooses the resource record set for ap-southeast-2.
Amazon Route 53 again selects a resource record set based on weight, and then checks the health of the selected resource record set. The health check passed, so Amazon Route 53 returns the applicable value in response to the query.
What Happens When You Associate a Health Check with an Alias Resource Record Set?
You can associate a health check with an alias resource record set instead of or in addition to setting the value of Evaluate Target Health to Yes. However, it's generally more useful if Amazon Route 53 responds to queries based on the health of the underlying resourcesג€"the HTTP servers, database servers, and other resources that your alias resource record sets refer to. For example, suppose the following configuration:
You assign a health check to a latency alias resource record set for which the alias target is a group of weighted resource record sets.
You set the value of Evaluate Target Health to Yes for the latency alias resource record set.
In this configuration, both of the following must be true before Amazon Route 53 will return the applicable value for a weighted resource record set:
The health check associated with the latency alias resource record set must pass.
At least one weighted resource record set must be considered healthy, either because it's associated with a health check that passes or because it's not associated with a health check. In the latter case, Amazon Route 53 always considers the weighted resource record set healthy.
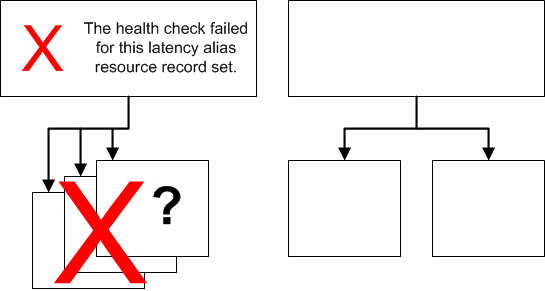
If the health check for the latency alias resource record set fails, Amazon Route 53 stops responding to queries using any of the weighted resource record sets in the alias target, even if they're all healthy. Amazon Route 53 doesn't know the status of the weighted resource record sets because it never looks past the failed health check on the alias resource record set.
What Happens When You Omit Health Checks?
In a complex configuration, it's important to associate health checks with all of the non-alias resource record sets. Let's return to the preceding example, but assume that a health check is missing on one of the weighted resource record sets in the us-east-1 region:

Here's what happens when you omit a health check on a non-alias resource record set in this configuration:
Amazon Route 53 receives a query for example.com. Based on the latency for the user making the request, Amazon Route 53 selects the latency alias resource record set for the us-east-1 region.
Amazon Route 53 looks up the alias target for the latency alias resource record set, and checks the status of the corresponding health checks. The health check for one weighted resource record set failed, so that resource record set is omitted from consideration.
The other weighted resource record set in the alias target for the us-east-1 region has no health check. The corresponding resource might or might not be healthy, but without a health check, Amazon Route 53 has no way to know. Amazon Route 53 assumes that the resource is healthy and returns the applicable value in response to the query.
What Happens When You Set Evaluate Target Health to No?
In general, you also want to set Evaluate Target Health to Yes for all of the alias resource record sets. In the following example, all of the weighted resource record sets have associated health checks, but Evaluate Target Health is set to No for the latency alias resource record set for the us-east-1 region:

Here's what happens when you set Evaluate Target Health to No for an alias resource record set in this configuration:
Amazon Route 53 receives a query for example.com. Based on the latency for the user making the request, Amazon Route 53 selects the latency alias resource record set for the us-east-1 region.
Amazon Route 53 determines what the alias target is for the latency alias resource record set, and checks the corresponding health checks. They're both failing.
Because the value of Evaluate Target Health is No for the latency alias resource record set for the us-east-1 region, Amazon Route 53 must choose one resource record set in this branch instead of backing out of the branch and looking for a healthy resource record set in the ap-southeast-2 region.
Question 2
Your startup wants to implement an order fulfillment process for selling a personalized gadget that needs an average of 3-4 days to produce with some orders taking up to 6 months you expect 10 orders per day on your first day. 1000 orders per day after 6 months and 10,000 orders after 12 months.
Orders coming in are checked for consistency men dispatched to your manufacturing plant for production quality control packaging shipment and payment processing If the product does not meet the quality standards at any stage of the process employees may force the process to repeat a step Customers are notified via email about order status and any critical issues with their orders such as payment failure.
Your base architecture includes AWS Elastic Beanstalk for your website with an RDS MySQL instance for customer data and orders.
How can you implement the order fulfillment process while making sure that the emails are delivered reliably?
- A. Add a business process management application to your Elastic Beanstalk app servers and re-use the ROS database for tracking order status use one of the Elastic Beanstalk instances to send emails to customers.
- B. Use SWF with an Auto Scaling group of activity workers and a decider instance in another Auto Scaling group with min/max=1 Use the decider instance to send emails to customers.
- C. Use SWF with an Auto Scaling group of activity workers and a decider instance in another Auto Scaling group with min/max=1 use SES to send emails to customers.
- D. Use an SQS queue to manage all process tasks Use an Auto Scaling group of EC2 Instances that poll the tasks and execute them. Use SES to send emails to customers.
Answer : C
Question 3
A read only news reporting site with a combined web and application tier and a database tier that receives large and unpredictable traffic demands must be able to respond to these traffic fluctuations automatically.
What AWS services should be used meet these requirements?
- A. Stateless instances for the web and application tier synchronized using ElastiCache Memcached in an autoscaimg group monitored with CloudWatch and RDS with read replicas.
- B. Stateful instances for the web and application tier in an autoscaling group monitored with CloudWatch and RDS with read replicas.
- C. Stateful instances for the web and application tier in an autoscaling group monitored with CloudWatch and multi-AZ RDS.
- D. Stateless instances for the web and application tier synchronized using ElastiCache Memcached in an autoscaling group monitored with CloudWatch and multi-AZ RDS.
Answer : A
Question 4
You are designing a photo-sharing mobile app. The application will store all pictures in a single Amazon S3 bucket.
Users will upload pictures from their mobile device directly to Amazon S3 and will be able to view and download their own pictures directly from Amazon S3.
You want to configure security to handle potentially millions of users in the most secure manner possible.
What should your server-side application do when a new user registers on the photo-sharing mobile application?
- A. Create an IAM user. Update the bucket policy with appropriate permissions for the IAM user. Generate an access key and secret key for the IAM user, store them in the mobile app and use these credentials to access Amazon S3.
- B. Create an IAM user. Assign appropriate permissions to the IAM user. Generate an access key and secret key for the IAM user, store them in the mobile app and use these credentials to access Amazon S3.
- C. Create a set of long-term credentials using AWS Security Token Service with appropriate permissions. Store these credentials in the mobile app and use them to access Amazon S3.
- D. Record the user's information in Amazon RDS and create a role in IAM with appropriate permissions. When the user uses their mobile app, create temporary credentials using the AWS Security Token Service "AssumeRole" function. Store these credentials in the mobile appג€™s memory and use them to access Amazon S3. Generate new credentials the next time the user runs the mobile app.
- E. Record the user's information in Amazon DynamoDB. When the user uses their mobile app, create temporary credentials using AWS Security Token Service with appropriate permissions. Store these credentials in the mobile app's memory and use them to access Amazon S3. Generate new credentials the next time the user runs the mobile app.
Answer : D
Explanation:
We can use either RDS or DynamoDB, however in our given answers, IAM role is mentioned only with RDS, so I would go with Answer B. Question was explicitly focused on security, so IAM with RDS is the best choice.
Question 5
You are tasked with moving a legacy application from a virtual machine running inside your datacenter to an Amazon VPC. Unfortunately, this app requires access to a number of on-premises services and no one who configured the app still works for your company. Even worse there's no documentation for it.
What will allow the application running inside the VPC to reach back and access its internal dependencies without being reconfigured? (Choose three.)
- A. An AWS Direct Connect link between the VPC and the network housing the internal services.
- B. An Internet Gateway to allow a VPN connection.
- C. An Elastic IP address on the VPC instance
- D. An IP address space that does not conflict with the one on-premises
- E. Entries in Amazon Route 53 that allow the Instance to resolve its dependencies' IP addresses
- F. A VM Import of the current virtual machine
Answer : ADF
Explanation:
AWS Direct Connect -
AWS Direct Connect makes it easy to establish a dedicated network connection from your premises to AWS. Using AWS Direct Connect, you can establish private connectivity between AWS and your datacenter, office, or collocation environment, which in many cases can reduce your network costs, increase bandwidth throughput, and provide a more consistent network experience than Internet-based connections.
AWS Direct Connect lets you establish a dedicated network connection between your network and one of the AWS Direct Connect locations. Using industry standard 802.1q VLANs, this dedicated connection can be partitioned into multiple virtual interfaces. This allows you to use the same connection to access public resources such as objects stored in Amazon S3 using public IP address space, and private resources such as Amazon EC2 instances running within an
Amazon -
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
using private IP space, while maintaining network separation between the public and private environments. Virtual interfaces can be reconfigured at any time to meet your changing needs.
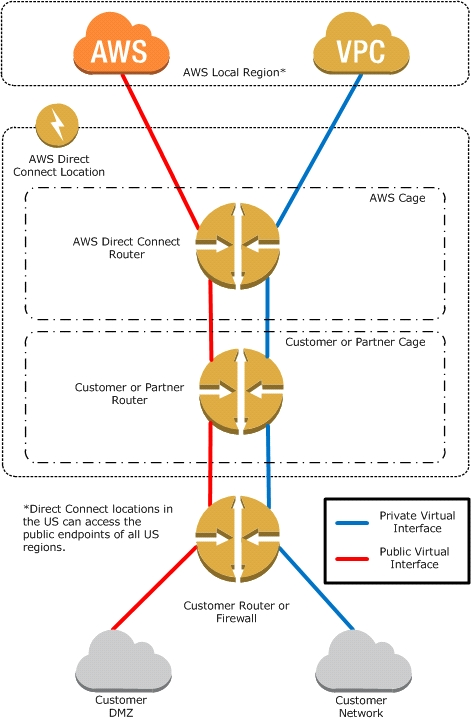
What is AWS Direct Connect?
AWS Direct Connect links your internal network to an AWS Direct Connect location over a standard 1 gigabit or 10 gigabit Ethernet fiber-optic cable. One end of the cable is connected to your router, the other to an AWS Direct Connect router. With this connection in place, you can create virtual interfaces directly to the
AWS cloud (for example, to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) and Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and to Amazon Virtual Private
Cloud (Amazon VPC), bypassing Internet service providers in your network path. An AWS Direct Connect location provides access to Amazon Web Services in the region it is associated with, as well as access to other US regions. For example, you can provision a single connection to any AWS Direct Connect location in the US and use it to access public AWS services in all US Regions and AWS GovCloud (US).
The following diagram shows how AWS Direct Connect interfaces with your network.
Requirements -
To use AWS Direct Connect, your network must meet one of the following conditions:
Your network is collocated with an existing AWS Direct Connect location. For more information on available AWS Direct Connect locations, go to http:// aws.amazon.com/directconnect/
.
You are working with an AWS Direct Connect partner who is a member of the AWS Partner Network (APN). For a list of AWS Direct Connect partners who can help you connect, go to http://aws.amazon.com/directconnect
.
You are working with an independent service provider to connect to AWS Direct Connect.
In addition, your network must meet the following conditions:
Connections to AWS Direct Connect require single mode fiber, 1000BASE-LX (1310nm) for 1 gigabit Ethernet, or 10GBASE-LR (1310nm) for 10 gigabit Ethernet.
Auto Negotiation for the port must be disabled. You must support 802.1Q VLANs across these connections.
Your network must support Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and BGP MD5 authentication. Optionally, you may configure Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
(BFD).
To connect to Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), you must first do the following:
Provide a private Autonomous System Number (ASN). Amazon allocates a private IP address in the 169.x.x.x range to you.
Create a virtual private gateway and attach it to your VPC. For more information about creating a virtual private gateway, see
Adding a Hardware Virtual Private
Gateway to Your VPC -
in the Amazon VPC User Guide.
To connect to public AWS products such as Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3, you need to provide the following:
A public ASN that you own (preferred) or a private ASN.
Public IP addresses (/31) (that is, one for each end of the BGP session) for each BGP session. If you do not have public IP addresses to assign to this connection, log on to AWS and then open a ticket with AWS Support
.
The public routes that you will advertise over BGP.
Question 6
You have a periodic image analysis application that gets some files in input, analyzes them and tor each file writes some data in output to a ten file the number of files in input per day is high and concentrated in a few hours of the day.
Currently you have a server on EC2 with a large EBS volume that hosts the input data and the results. It takes almost 20 hours per day to complete the process.
What services could be used to reduce the elaboration time and improve the availability of the solution?
- A. S3 to store I/O files. SQS to distribute elaboration commands to a group of hosts working in parallel. Auto scaling to dynamically size the group of hosts depending on the length of the SQS queue
- B. EBS with Provisioned IOPS (PIOPS) to store I/O files. SNS to distribute elaboration commands to a group of hosts working in parallel Auto Scaling to dynamically size the group of hosts depending on the number of SNS notifications
- C. S3 to store I/O files, SNS to distribute evaporation commands to a group of hosts working in parallel. Auto scaling to dynamically size the group of hosts depending on the number of SNS notifications
- D. EBS with Provisioned IOPS (PIOPS) to store I/O files SQS to distribute elaboration commands to a group of hosts working in parallel Auto Scaling to dynamically size the group ot hosts depending on the length of the SQS queue.
Answer : D
Explanation:
Amazon EBS allows you to create storage volumes and attach them to Amazon EC2 instances. Once attached, you can create a file system on top of these volumes, run a database, or use them in any other way you would use a block device. Amazon EBS volumes are placed in a specific Availability Zone, where they are automatically replicated to protect you from the failure of a single component.
Amazon EBS provides three volume types: General Purpose (SSD), Provisioned IOPS (SSD), and Magnetic. The three volume types differ in performance characteristics and cost, so you can choose the right storage performance and price for the needs of your applications. All EBS volume types offer the same durable snapshot capabilities and are designed for 99.999% availability.
Question 7
You have been asked to design the storage layer for an application. The application requires disk performance of at least 100,000 IOPS. In addition, the storage layer must be able to survive the loss of an individual disk, EC2 instance, or Availability Zone without any data loss. The volume you provide must have a capacity of at least 3 TB.
Which of the following designs will meet these objectives?
- A. Instantiate a c3.8xlarge instance in us-east-1. Provision 4x1TB EBS volumes, attach them to the instance, and configure them as a single RAID 5 volume. Ensure that EBS snapshots are performed every 15 minutes.
- B. Instantiate a c3.8xlarge instance in us-east-1. Provision 3xlTB EBS volumes, attach them to the Instance, and configure them as a single RAID 0 volume. Ensure that EBS snapshots are performed every 15 minutes.
- C. Instantiate an i2.8xlarge instance in us-east-1a. Create a RAID 0 volume using the four 800GB SSD ephemeral disks provided with the instance. Provision 3x1TB EBS volumes, attach them to the instance, and configure them as a second RAID 0 volume. Configure synchronous, block-level replication from the ephemeral-backed volume to the EBS-backed volume.
- D. Instantiate a c3.8xlarge instance in us-east-1. Provision an AWS Storage Gateway and configure it for 3 TB of storage and 100,000 IOPS. Attach the volume to the instance.
- E. Instantiate an i2.8xlarge instance in us-east-1a. Create a RAID 0 volume using the four 800GB SSD ephemeral disks provided with the instance. Configure synchronous, block-level replication to an identically configured instance in us-east-1b.
Answer : E
Reference:
https://acloud.guru/course/aws-certified-solutions-architect-associate/discuss/-KJdi4tFMp2x_O88J6U4/an-architecture-design-question
Question 8
You are the new IT architect in a company that operates a mobile sleep tracking application.
When activated at night, the mobile app is sending collected data points of 1 kilobyte every 5 minutes to your backend.
The backend takes care of authenticating the user and writing the data points into an Amazon DynamoDB table.
Every morning, you scan the table to extract and aggregate last night's data on a per user basis, and store the results in Amazon S3. Users are notified via
Amazon SNS mobile push notifications that new data is available, which is parsed and visualized by the mobile app.
Currently you have around 100k users who are mostly based out of North America.
You have been tasked to optimize the architecture of the backend system to lower cost.
What would you recommend? (Choose two.)
- A. Have the mobile app access Amazon DynamoDB directly Instead of JSON files stored on Amazon S3.
- B. Write data directly into an Amazon Redshift cluster replacing both Amazon DynamoDB and Amazon S3.
- C. Introduce an Amazon SQS queue to buffer writes to the Amazon DynamoDB table and reduce provisioned write throughput.
- D. Introduce Amazon Elasticache to cache reads from the Amazon DynamoDB table and reduce provisioned read throughput.
- E. Create a new Amazon DynamoDB table each day and drop the one for the previous day after its data is on Amazon S3.
Answer : CD
Reference:
https://d0.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/performance-at-scale-with-amazon-elasticache.pdf
Question 9
A large real-estate brokerage is exploring the option of adding a cost-effective location based alert to their existing mobile application. The application backend infrastructure currently runs on AWS. Users who opt in to this service will receive alerts on their mobile device regarding real-estate otters in proximity to their location. For the alerts to be relevant delivery time needs to be in the low minute count the existing mobile app has 5 million users across the US.
Which one of the following architectural suggestions would you make to the customer?
- A. The mobile application will submit its location to a web service endpoint utilizing Elastic Load Balancing and EC2 instances; DynamoDB will be used to store and retrieve relevant offers EC2 instances will communicate with mobile earners/device providers to push alerts back to mobile application.
- B. Use AWS DirectConnect or VPN to establish connectivity with mobile carriers EC2 instances will receive the mobile applications location through carrier connection: RDS will be used to store and relevant offers. EC2 instances will communicate with mobile carriers to push alerts back to the mobile application.
- C. The mobile application will send device location using SQS. EC2 instances will retrieve the relevant others from DynamoDB. AWS Mobile Push will be used to send offers to the mobile application.
- D. The mobile application will send device location using AWS Mobile Push EC2 instances will retrieve the relevant offers from DynamoDB. EC2 instances will communicate with mobile carriers/device providers to push alerts back to the mobile application.
Answer : C
Question 10
You currently operate a web application. In the AWS US-East region. The application runs on an auto-scaled layer of EC2 instances and an RDS Multi-AZ database. Your IT security compliance officer has tasked you to develop a reliable and durable logging solution to track changes made to your EC2.IAM And RDS resources. The solution must ensure the integrity and confidentiality of your log data.
Which of these solutions would you recommend?
- A. Create a new CloudTrail trail with one new S3 bucket to store the logs and with the global services option selected. Use IAM roles S3 bucket policies and Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) Delete on the S3 bucket that stores your logs.
- B. Create a new CloudTrail with one new S3 bucket to store the logs Configure SNS to send log file delivery notifications to your management system. Use IAM roles and S3 bucket policies on the S3 bucket mat stores your logs.
- C. Create a new CloudTrail trail with an existing S3 bucket to store the logs and with the global services option selected. Use S3 ACLs and Multi Factor Authentication (MFA). Delete on the S3 bucket that stores your logs.
- D. Create three new CloudTrail trails with three new S3 buckets to store the logs one for the AWS Management console, one for AWS SDKs and one for command line tools. Use IAM roles and S3 bucket policies on the S3 buckets that store your logs.
Answer : A
Question 11
Your department creates regular analytics reports from your company's log files All log data is collected in Amazon S3 and processed by daily Amazon Elastic
MapReduce (EMR) jobs that generate daily PDF reports and aggregated tables in CSV format for an Amazon Redshift data warehouse.
Your CFO requests that you optimize the cost structure for this system.
Which of the following alternatives will lower costs without compromising average performance of the system or data integrity for the raw data?
- A. Use reduced redundancy storage (RRS) for all data In S3. Use a combination of Spot Instances and Reserved Instances for Amazon EMR jobs. Use Reserved Instances for Amazon Redshift.
- B. Use reduced redundancy storage (RRS) for PDF and .csv data in S3. Add Spot Instances to EMR jobs. Use Spot Instances for Amazon Redshift.
- C. Use reduced redundancy storage (RRS) for PDF and .csv data In Amazon S3. Add Spot Instances to Amazon EMR jobs. Use Reserved Instances for Amazon Redshift.
- D. Use reduced redundancy storage (RRS) for all data in Amazon S3. Add Spot Instances to Amazon EMR jobs. Use Reserved Instances for Amazon Redshift.
Answer : C
Explanation:
Using Reduced Redundancy Storage Amazon S3 stores objects according to their storage class. It assigns the storage class to an object when it is written to
Amazon S3. You can assign objects a specific storage class (standard or reduced redundancy) only when you write the objects to an Amazon S3 bucket or when you copy objects that are already stored in Amazon S3. Standard is the default storage class. For information about storage classes, see
Object Key and -
Metadata -
.
In order to reduce storage costs, you can use reduced redundancy storage for noncritical, reproducible data at lower levels of redundancy than Amazon S3 provides with standard storage. The lower level of redundancy results in less durability and availability, but in many cases, the lower costs can make reduced redundancy storage an acceptable storage solution. For example, it can be a cost-effective solution for sharing media content that is durably stored elsewhere. It can also make sense if you are storing thumbnails and other resized images that can be easily reproduced from an original image.
Reduced redundancy storage is designed to provide 99.99% durability of objects over a given year. This durability level corresponds to an average annual expected loss of 0.01% of objects. For example, if you store 10,000 objects using the RRS option, you can, on average, expect to incur an annual loss of a single object per year (0.01% of 10,000 objects).
Note:
This annual loss represents an expected average and does not guarantee the loss of less than 0.01% of objects in a given year.
Reduced redundancy storage stores objects on multiple devices across multiple facilities, providing 400 times the durability of a typical disk drive, but it does not replicate objects as many times as Amazon S3 standard storage. In addition, reduced redundancy storage is designed to sustain the loss of data in a single facility.
If an object in reduced redundancy storage has been lost, Amazon S3 will return a 405 error on requests made to that object. Amazon S3 also offers notifications for reduced redundancy storage object loss: you can configure your bucket so that when Amazon S3 detects the loss of an RRS object, a notification will be sent through Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS). You can then replace the lost object. To enable notifications, you can use the Amazon S3 console to set the Notifications property of your bucket.
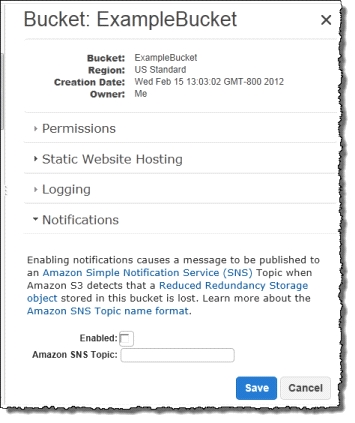
Question 12
You require the ability to analyze a large amount of data, which is stored on Amazon S3 using Amazon Elastic Map Reduce. You are using the cc2 8xlarge instance type, whose CPUs are mostly idle during processing. Which of the below would be the most cost efficient way to reduce the runtime of the job?
- A. Create more, smaller flies on Amazon S3.
- B. Add additional cc2 8xlarge instances by introducing a task group.
- C. Use smaller instances that have higher aggregate I/O performance.
- D. Create fewer, larger files on Amazon S3.
Answer : C
Question 13
An AWS customer is deploying an application mat is composed of an AutoScaling group of EC2 Instances.
The customers security policy requires that every outbound connection from these instances to any other service within the customers Virtual Private Cloud must be authenticated using a unique x 509 certificate that contains the specific instance-id.
In addition, an x 509 certificates must Designed by the customer's Key management service in order to be trusted for authentication.
Which of the following configurations will support these requirements?
- A. Configure an IAM Role that grants access to an Amazon S3 object containing a signed certificate and configure the Auto Scaling group to launch instances with this role. Have the instances bootstrap get the certificate from Amazon S3 upon first boot.
- B. Embed a certificate into the Amazon Machine Image that is used by the Auto Scaling group. Have the launched instances generate a certificate signature request with the instance's assigned instance-id to the key management service for signature.
- C. Configure the Auto Scaling group to send an SNS notification of the launch of a new instance to the trusted key management service. Have the Key management service generate a signed certificate and send it directly to the newly launched instance.
- D. Configure the launched instances to generate a new certificate upon first boot. Have the Key management service poll the Auto Scaling group for associated instances and send new instances a certificate signature (hat contains the specific instance-id.
Answer : A
Question 14
Your company runs a customer facing event registration site This site is built with a 3-tier architecture with web and application tier servers and a MySQL database The application requires 6 web tier servers and 6 application tier servers for normal operation, but can run on a minimum of 65% server capacity and a single MySQL database.
When deploying this application in a region with three availability zones (AZs) which architecture provides high availability?
- A. A web tier deployed across 2 AZs with 3 EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instances in each AZ inside an Auto Scaling Group behind an ELB (elastic load balancer), and an application tier deployed across 2 AZs with 3 EC2 instances in each AZ inside an Auto Scaling Group behind an ELB and one RDS (Relational Database Service) instance deployed with read replicas in the other AZ.
- B. A web tier deployed across 3 AZs with 2 EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instances in each AZ inside an Auto Scaling Group behind an ELB (elastic load balancer) and an application tier deployed across 3 AZs with 2 EC2 instances in each AZ inside an Auto Scaling Group behind an ELB and one RDS (Relational Database Service) Instance deployed with read replicas in the two other AZs.
- C. A web tier deployed across 2 AZs with 3 EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instances in each AZ inside an Auto Scaling Group behind an ELB (elastic load balancer) and an application tier deployed across 2 AZs with 3 EC2 instances m each AZ inside an Auto Scaling Group behind an ELS and a Multi-AZ RDS (Relational Database Service) deployment.
- D. A web tier deployed across 3 AZs with 2 EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instances in each AZ Inside an Auto Scaling Group behind an ELB (elastic load balancer). And an application tier deployed across 3 AZs with 2 EC2 instances in each AZ inside an Auto Scaling Group behind an ELB and a Multi-AZ RDS (Relational Database services) deployment.
Answer : MySQLD
Explanation:
Amazon RDS Multi-AZ Deployments -
Amazon RDS Multi-AZ deployments provide enhanced availability and durability for Database (DB) Instances, making them a natural fit for production database workloads. When you provision a Multi-AZ DB Instance, Amazon RDS automatically creates a primary DB Instance and synchronously replicates the data to a standby instance in a different Availability Zone (AZ). Each AZ runs on its own physically distinct, independent infrastructure, and is engineered to be highly reliable. In case of an infrastructure failure (for example, instance hardware failure, storage failure, or network disruption), Amazon RDS performs an automatic failover to the standby, so that you can resume database operations as soon as the failover is complete. Since the endpoint for your DB Instance remains the same after a failover, your application can resume database operation without the need for manual administrative intervention.
Enhanced Durability -
Multi-AZ deployments for the -
,
Oracle -
, and
PostgreSQL -
engines utilize synchronous physical replication to keep data on the standby up-to-date with the primary. Multi-AZ deployments for the
SQL Server -
engine use synchronous logical replication to achieve the same result, employing SQL Server-native Mirroring technology. Both approaches safeguard your data in the event of a DB Instance failure or loss of an Availability Zone.
If a storage volume on your primary fails in a Multi-AZ deployment, Amazon RDS automatically initiates a failover to the up-to-date standby. Compare this to a
Single-AZ deployment: in case of a Single-AZ database failure, a user-initiated point-in-time-restore operation will be required. This operation can take several hours to complete, and any data updates that occurred after the latest restorable time (typically within the last five minutes) will not be available.
Amazon Aurora -
employs a highly durable, SSD-backed virtualized storage layer purpose-built for database workloads. Amazon Aurora automatically replicates your volume six ways, across three Availability Zones. Amazon Aurora storage is fault-tolerant, transparently handling the loss of up to two copies of data without affecting database write availability and up to three copies without affecting read availability. Amazon Aurora storage is also self-healing. Data blocks and disks are continuously scanned for errors and replaced automatically.
Increased Availability -
You also benefit from enhanced database availability when running Multi-AZ deployments. If an Availability Zone failure or DB Instance failure occurs, your availability impact is limited to the time automatic failover takes to complete: typically under one minute for Amazon Aurora and one to two minutes for other database engines (see the
RDS FAQ -
for details).
The availability benefits of Multi-AZ deployments also extend to planned maintenance and backups. In the case of system upgrades like OS patching or DB
Instance scaling, these operations are applied first on the standby, prior to the automatic failover. As a result, your availability impact is, again, only the time required for automatic failover to complete.
Unlike Single-AZ deployments, I/O activity is not suspended on your primary during backup for Multi-AZ deployments for the MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL engines, because the backup is taken from the standby. However, note that you may still experience elevated latencies for a few minutes during backups for Multi-
AZ deployments.
On instance failure in Amazon Aurora deployments, Amazon RDS uses RDS Multi-AZ technology to automate failover to one of up to 15 Amazon Aurora Replicas you have created in any of three Availability Zones. If no Amazon Aurora Replicas have been provisioned, in the case of a failure, Amazon RDS will attempt to create a new Amazon Aurora DB instance for you automatically.
Question 15
Your customer wishes to deploy an enterprise application to AWS, which will consist of several web servers, several application servers and a small (50GB)
Oracle database. Information is stored, both in the database and the file systems of the various servers. The backup system must support database recovery whole server and whole disk restores, and individual file restores with a recovery time of no more than two hours. They have chosen to use RDS Oracle as the database.
Which backup architecture will meet these requirements?
- A. Backup RDS using automated daily DB backups. Backup the EC2 instances using AMIs and supplement with file-level backup to S3 using traditional enterprise backup software to provide file level restore.
- B. Backup RDS using a Multi-AZ Deployment. Backup the EC2 instances using Amis, and supplement by copying file system data to S3 to provide file level restore.
- C. Backup RDS using automated daily DB backups. Backup the EC2 instances using EBS snapshots and supplement with file-level backups to Amazon Glacier using traditional enterprise backup software to provide file level restore.
- D. Backup RDS database to S3 using Oracle RMAN. Backup the EC2 instances using Amis, and supplement with EBS snapshots for individual volume restore.
Answer : A
Explanation:
Point-In-Time Recovery -
In addition to the daily automated backup, Amazon RDS archives database change logs. This enables you to recover your database to any point in time during the backup retention period, up to the last five minutes of database usage.
Amazon RDS stores multiple copies of your data, but for Single-AZ DB instances these copies are stored in a single availability zone. If for any reason a Single-AZ
DB instance becomes unusable, you can use point-in-time recovery to launch a new DB instance with the latest restorable data. For more information on working with point-in-time recovery, go to
Restoring a DB Instance to a Specified Time
.
Note -
Multi-AZ deployments store copies of your data in different Availability Zones for greater levels of data durability. For more information on Multi-AZ deployments, see
High Availability (Multi-AZ)
.